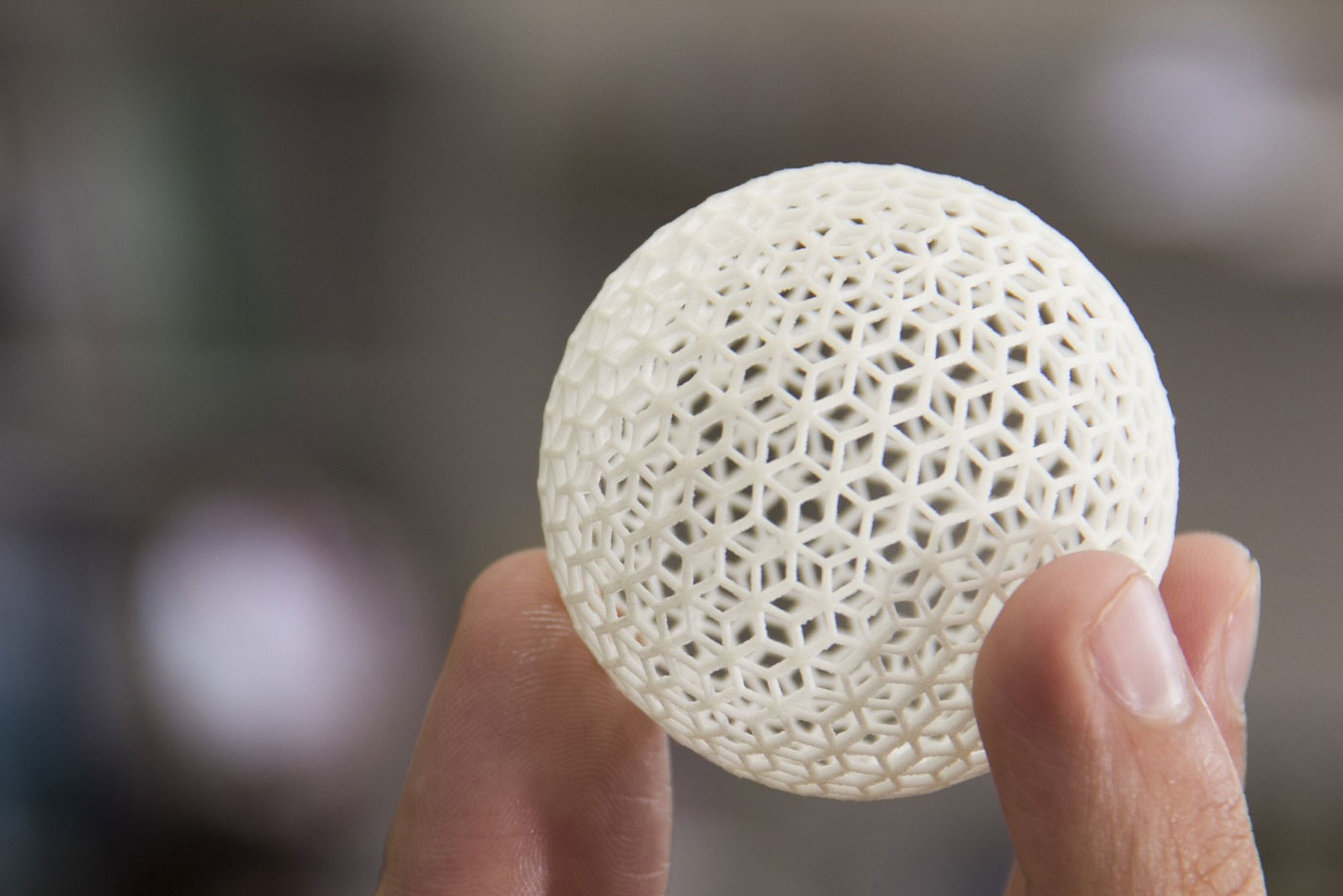
The field of additive manufacturing, as 3D printing is usually called in an industrial context, has grown exponentially in recent years. Three-dimensional objects are created by applying material layer by layer.
At the same time, the requirements regarding the protection of the devices from heat are increasing. Heat build-up should be avoided as far as possible, as theycan have an extremely negative effect:
- Parts of machines can be destroyed
- the service life is reduced
- costs are rising
3D Printing: How It Works and Benefits

In 3D printing, a component is built up layered by fusing or curing amedium. The fusion of metal powder is usually achieved with laser beams, the curing of resins with an exposure unit. The more constant the operating temperature of the laser or exposure unit, the more precise the resultof the printedmodel.
3D printing is a high-precision technology that delivers high-quality printing results – the cooling of the devices must therefore be correspondingly precise, temperature-stable and reliable.
Thereare four main advantages to this:
- the effort in post-processing is lower
- Longer service life of the laser or light source
- lower costs
- shorter delivery time
With FDM(Fused Deposition Modeling, which is printing with plastic filament Dra Ht),water cooling may also berequired if, for example, motors to drive the axles, the nozzles or the installation space itself have to be cooled.
Overall, the technologies of 3D printing bring great advantages in terms of efficiency,quality, costs and delivery times.
Where is 3D printing used?
Depending on the printing technology, different industries are served. Areas of application include: industry, model making, research, construction and medicine.
Classic materials for 3D printing are plastics, synthetic resins, ceramics and specially prepared metals.
The most established additive manufacturing processes include: stereolithography, laser sintering, laser beam melting, electron beam melting andmuch more.
The printing of ceramics is mainly used in the aerospace industry for the production of turbine motors as well as in medical technology, for example for the production of dental implants.
In the field of finishing (which includes all processesthat come after production in 3D printing) in metallic 3D printing, the aim is to cool the heat generated in the chemical post-treatment process in the acid baths.
Cooling systems from SMC
At SMC, we have been producing cooling machines since1978, and our cooling systems have evolved over the years with the requirements and needs of our customers. SMC devices stand out for their high reliability (24/7 operation without failures) and temperature stability.
You will find various cooling solutions with us, including
- Standard cooler
- Rack Mount Coolers
- Dual Channel Coolers
- High-level coolers

We accompany our customers from the starting signal to the completion of a project: From the first calculation to on-site tests, includingselecting the right cooler, to installation and commissioning.
When working together, you benefit from our global support, as we are represented in more than 80 countries. In addition, you can reduce the number of suppliers because we are at your disposal as a complete supplier (cooling, pneumatics, fittings, hoses).
Would you like to learn more about our possibilities in the field of cooling and temperature control in 3D printing?
Contact us – our team will be happy to answer your questions.

 DE
DE CZ
CZ HU
HU PL
PL SI
SI